Kinetic Modeling of Covalent Inhibition: Effects of Rapidly Fluctuating Intermediate States
Covalent Modifiers
JUNE 2, 2025
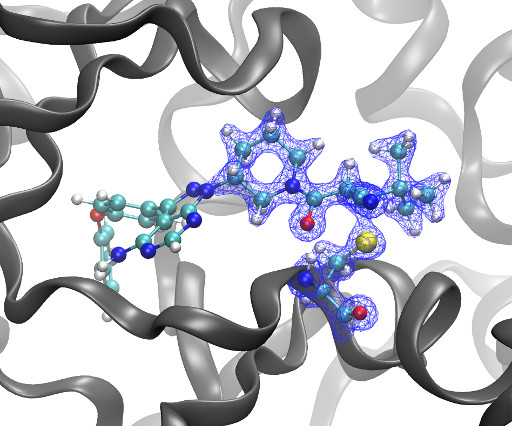
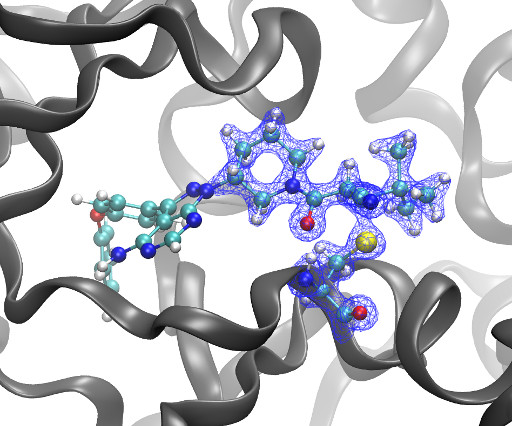
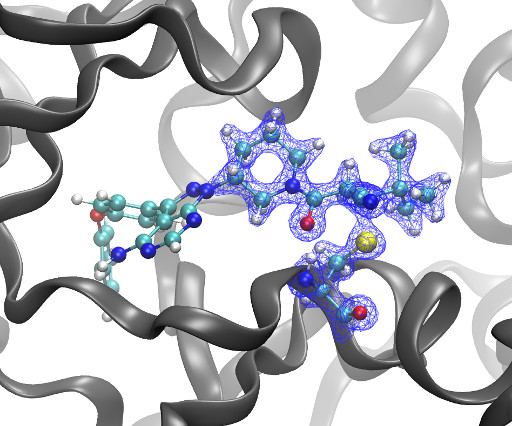
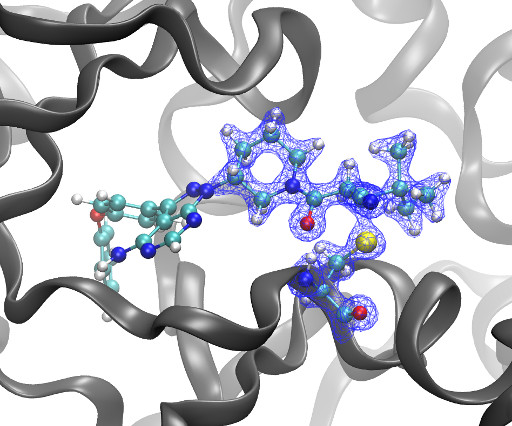
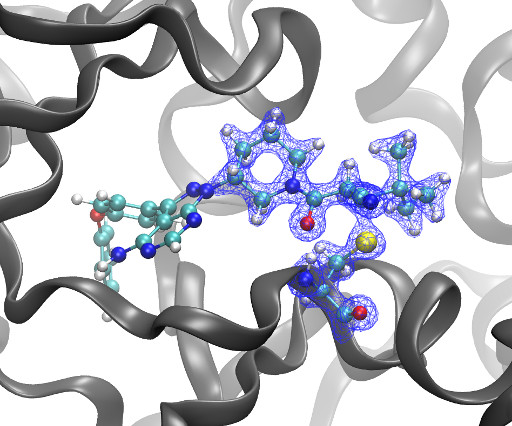
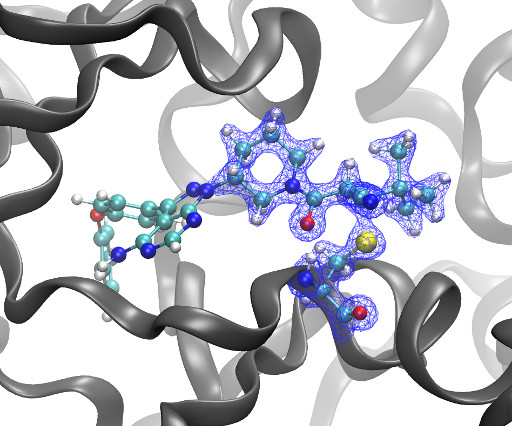
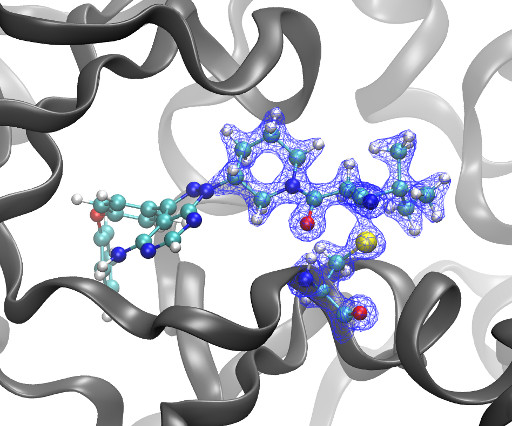
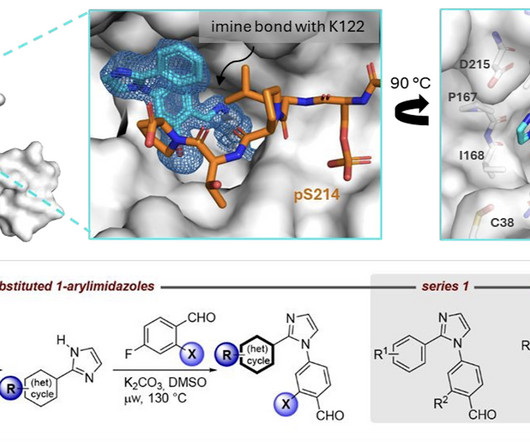
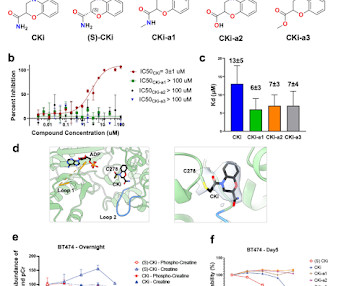
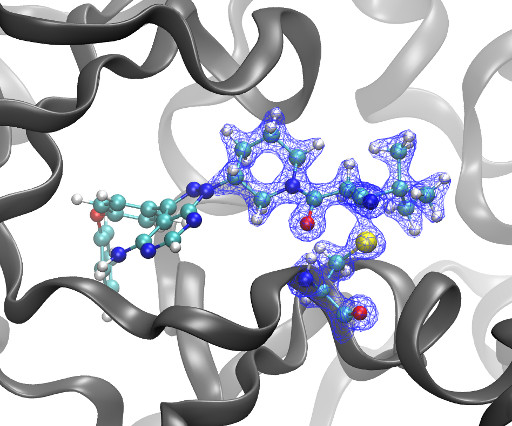
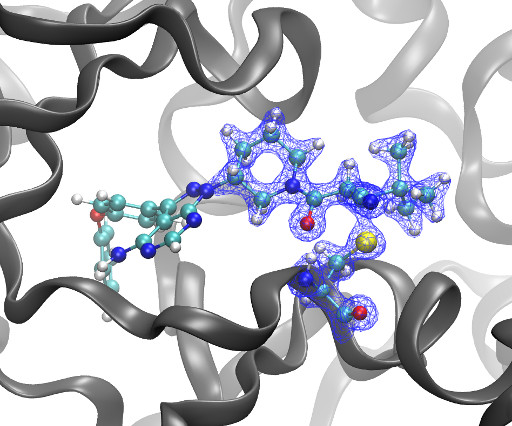
Kyle Ghaby, Benot Roux bioRxiv 2025.05.28.656658; doi: [link] There is increasing interest in the discovery of small-molecule inhibitors that form covalent bonds with their targets for therapeutic applications. Nevertheless, identifying clear rational design principles remains challenging because the action of these molecules cannot be understood as common noncovalent inhibitors.







Let's personalize your content